Things you need to know about antidepressants and pregnancy
Find out how to navigate the risks and benefits of antidepressants and pregnancy. Find out more about how to safely manage your mental health.
The topic of antidepressant use during pregnancy has been attracting more attention in recent years. The question of whether to quit taking antidepressants during pregnancy or to keep taking them is one that many expecting moms must decide.
Pregnant women are at risk of experiencing postnatal depression, which can lead to congenital disabilities, requiring careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers to ensure effective treatment.
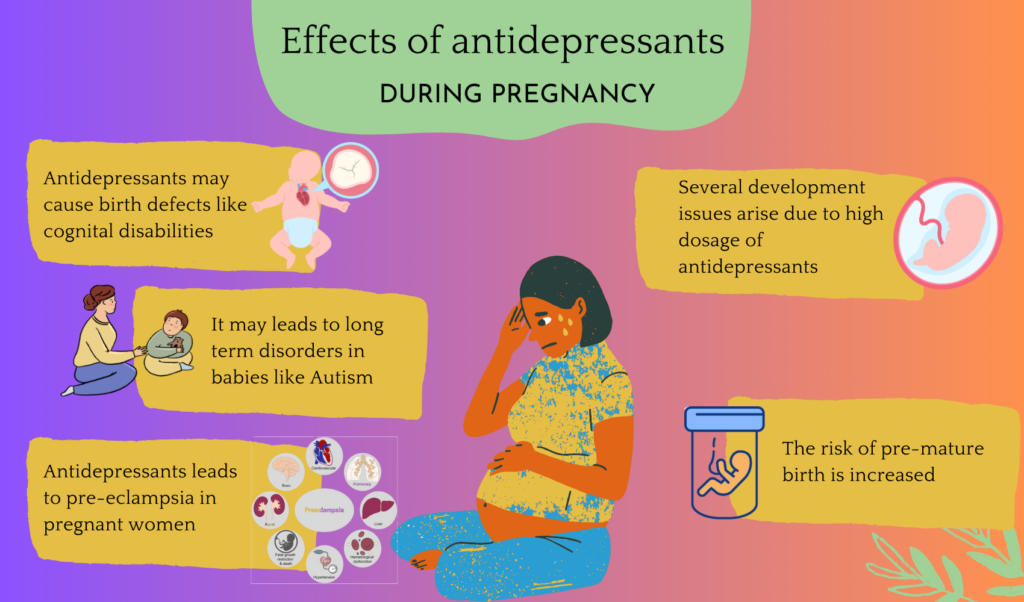
Why Avoid Antidepressants during Pregnancy
Depression during pregnancy can be a significant concern, with antidepressants like SSRIs potentially increasing the risk of low birth weight, congenital disabilities, and persistent pulmonary hypertension in new-borns.
However, some women may find the benefits of antidepressant treatment outweigh the risks. It is recommended to stop taking SSRIs in the first trimester and explore other treatment options if needed.
Risk of Birth Defects
Pregnant women taking antidepressants during pregnancy may face potential risks such as congenital disabilities and postnatal depression. SSRIs, commonly prescribed to treat depression, may increase the risk of complications like low birth weight and persistent pulmonary hypertension. It’s crucial to weigh the risks against untreated depression during pregnancy and work closely with healthcare providers to determine the best course of action.
Effect on the Development of the Baby
Depression during pregnancy can be managed with antidepressants, but their potential impact on a baby’s development is essential. Different types of antidepressants, such as tricyclic and SNRI, may be prescribed.Yet, untreated depression may be more harmful. Women should consult their healthcare provider to weigh the risks and benefits of antidepressants during pregnancy, considering both mother and baby’s mental health needs.
Increased chances of immature Birth
Pregnancy is a critical time for managing depression, and the use of antidepressants during pregnancy can pose significant risks. Utero exposure to these medications can lead to preterm Birth and potential relapse of depression. It is crucial to carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of antidepressant treatment to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
The effects of antidepressants on pregnancy and lactation, as well as the impact on breastfeeding, should also be considered. Despite some studies suggesting minimal effects, the long-term effects of antidepressants during pregnancy remain a concern.
Symptoms of Postpartum Removal
Pregnant women are at risk of experiencing potential risks from antidepressants, including withdrawal symptoms and an autism spectrum disorder. These risks can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, especially in high doses. It is crucial for pregnant women to consult with healthcare providers about the use of antidepressants and to weigh the benefits against potential risks to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Potential Long-Term Effects
Women taking antidepressants during pregnancy may be concerned about the possible long-term effects on their babies. Studies have shown that pregnancy was not associated with an increased per cent risk of neural tube defects for those undergoing antenatal and postnatal depression.
Neverthless, there is a potential risk of your baby developing these defects if you were to undergo antidepressant discontinuation during pregnancy. Additionally, drugs during pregnancy are linked to an increased risk of preterm Birth. On the other hand, treatment with antidepressants has been found to make women less likely to get antenatal and postnatal depression. It is essential to weigh the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Pre-eclampsia
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in monitoring blood pressure in pregnant women, a condition characterized by high blood pressure, protein in urine, and potential organ damage. Pregnant women should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their health, urine protein levels, and overall health throughout pregnancy to detect and manage pre-eclampsia, reducing potential risks for both mother and baby.
Speech development problems
The development of speech and language skills is influenced by various issues, including language disorders like stuttering, which can disrupt speech flow, causing frustration and social interactions. Early intervention is crucial to address these challenges and improve communication.
Increase the risk of child sedation.
Sedation of children for medical procedures raises risks, including respiratory depression, unintended side effects, and over-sedation due to their smaller size and metabolic rate. Parents and healthcare providers must weigh the benefits against risks and take necessary precautions to ensure child safety during sedation.
Alternative Medical Care & Counselling
To make well-informed healthcare decisions, it is essential to get a consultation from medical specialists before investigating alternative methods, including treatment, spinal adjustments, and natural remedies.
Alternative Treatment Options
Pregnancy can present potential risks to both mother and baby. Depression can be treated with alternative options like cognitive behavioural therapy, which is safe and effective. However, certain medications may have a 10% risk of neural tube defects. Considering all options with a healthcare provider is crucial for the best course of action.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals and providers play a crucial role in effectively treating patients. Open communication and trusting relationships between healthcare professionals and patients are essential for achieving optimal health outcomes and ensuring the best possible care.
Personalized Choice-Making
Personalized decision-making, based on individual preferences, is a specific approach to success. It ensures that individuals achieve outcomes that align with their particular objectives, leading to greater satisfaction and success in both personal and professional contexts.
Wrap up
In summary, managing the use of antidepressants throughout pregnancy might be difficult, but it’s critical to give your mental health and well-being priority. You may make decisions with confidence that support a healthy pregnancy and a happy ending for both you and your unborn child by being informed and asking for help from healthcare professionals. If you want a quick guide on writing baby shower wishes on a card, go through this post.







